Modern Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are special powerful desktop software systems initially oriented to adequately reflect and process geo-spatial information. Such systems can be successfully used as convenient instruments for training future engineers in all technical domains of spatially distributed objects presentation, projection and analysis. Particular experience of using GIS for telecommunications systems learning is presented in the paper.
One of the most important problems in technical education consists in the necessity to make right choices during selection of appropriate tools for best knowledge presentation from given domain or subject. It is recognized now, that object oriented, black-box systemologic approach is the most "natural" one because our minding tools are well adapted to make structured reflection of surrounding complex (synergetic) world, implementing Caesar's principle in studies: "Divide and dominate!".
Desktop Geographic Information Systems belongs to relatively new and very fast growing direction of modern information technologies. From our point of view GIS can serve as appropriate Media necessary to create convenient learning, presentation and exploring background for engineering and other branches of human activities. GIS must become a subject of interdisciplinary studies not only at engineering-oriented academic units but also at general studies chapters as well. As an example of growing popularity of GIS can serve the Microsoft Map plug-in recently included in the very popular Microsoft Office's tool Excel.
GIS can be successfully used as attractive learning platform, capable to precisely manipulate 2D/3D structured "real-reality" or "abstract-reality" space navigation media filled with objects from any geographically distributed engineering area. They can be programmed to run as demonstration of predetermined sequences of topics, interactive navigation at random choices selections base, knowledge level evaluation by questions and answers sessions.
GIS are integrated systems, containing very important alliance of special properties and facilities like:
Potentially GIS are perfect desktop instruments for using in various branches of engineering specialty applications: telecommunications, architecture, building design, water and power distribution, transport systems etc.
Telecommunications objects displacements are essentially distributed in a wide range of spaces that can be naturally simulated by GIS: rooms, buildings, campuses, villages, towns, countries, continents, geo-sphere and cosmos. It is necessary to teach future engineers in adequate modeling environments in order to educate them to be capable to sure manipulate spatially distributed objects using GIS tools.
Practical experience of MapInfo Professional GIS [1] introduction in the curriculum of "Wide Area Telecommunication Systems" studies at the Faculty of Radioelectronics from Technical University of Moldova includes next main topics:
A number of map layers was digitized, vectored, adjusted and filled with appropriate data, forming a block of such map stacks as:
MBG can serve as good starting point for general-purpose GIS studies while the TGV and TDV stacks are subjects of implementation during laboratory and individual student's work of appropriate specialties. For example, the structure of first hops of logical International Telecommunications links of Moldova is presented on the figure 1 using GIS map of Europe.
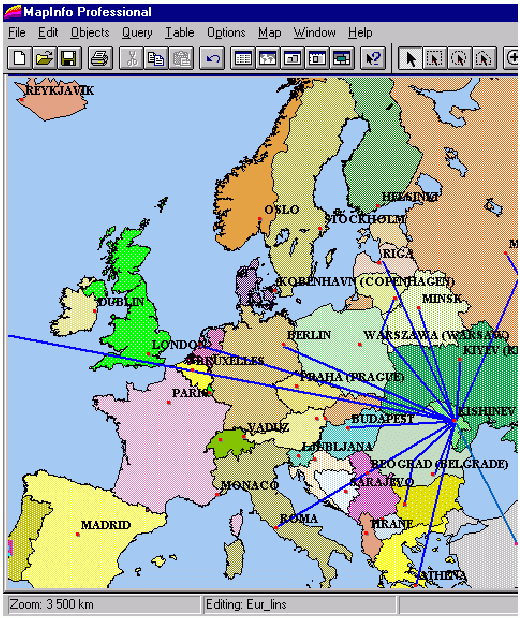
Fig.1. External logical links of telecommunications of Moldova
Both TGV and TDV level of presentation can be subdivided consequently into two kinds of stacks:
It interesting to notify, that data presentation tools of MapInfo GIS contains possibilities to create thematic maps graphically labeled with different table values, that can reflects wide range of parameters and statistics of telecommunications-oriented geo-objects like: relative and absolute values of traffic measures, frequency of errors and supercharges, levels of the quality of services etc.
An example of students projected TGV map of Moldova is presented on figure 2:
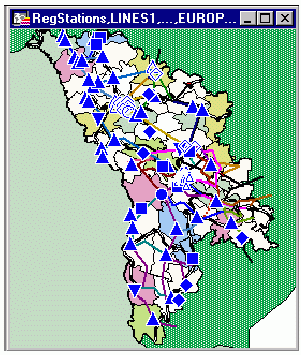
Fig.2. Example of TGV Map of Moldova
Concluding we can remark, that just first attempts to use GIS in technical high education system of Moldova has approved expected positive properties of such kind of information technology. The results of application of GIS for telecommunication systems presentation is expected to be used practically in Moldtelecom state company in order to implement top-level Management Interface software inside of MoldTMN: a project of new Nation-level Telecommunication Management Network.
Veaceslav Sidorenco.
Technical University of Moldova
Faculty of Radioelectronics
Stefan cel Mare, 168
Chisinau 2004
Moldova, Republic of
E-mail: svv@svv.mldnet.com
http://www.geocities.com/CapeCanaveral/7656